Courses by Software
Courses by Semester
Courses by Domain
Tool-focused Courses
Machine learning
POPULAR COURSES
Success Stories
Week 8 - Challenge 4 - Bumper
AIM Create the Bumper Plastic component through the given Class-A surface. To begin with, the tooling axis for the given Class-A Surface should be created meeting the requirements of the draft angle and at the end perform the Draft analysis on the model. INTRODUCTION A bumper is a structure attached to or integrated…
Karthik S
updated on 11 Dec 2022
AIM
Create the Bumper Plastic component through the given Class-A surface. To begin with, the tooling axis for the given Class-A Surface should be created meeting the requirements of the draft angle and at the end perform the Draft analysis on the model.
INTRODUCTION
A bumper is a structure attached to or integrated with the front and rear ends of a motor vehicle, to absorb impact in a minor collision, ideally minimizing repair costs.

They are designed to absorb impact to the front and rear of vehicles and minimize low-speed collision damage. Today, standard passenger vehicle bumpers have a rigid reinforcing bar under the outer cover, with sections of compressible foam or plastic underneath.
A bumper is made up of four parts:
- Bumper cover.
- The bumper absorber.
- The bumper reinforcement bar.
- The bumper mounting system.
The first car bumpers were created all the way back in 1901 and consisted of metal beams attached to the front and rear of the car to protect it during a low-speed collision. Designed to protect the expensive and fragile components like the headlights, tail lights, hood, exhaust, and cooling systems, early metal bumpers were focused on sheer resilience.
Modern consumer production cars have almost completely switched over to plastic bumpers. Modern car bumpers are made from thermoplastic olefins, a blend of plastic molecules, rubber, and a reinforcing filler like carbon fiber or calcium carbonate. This blend of materials creates a scratch and impact-resistant plastic that can bond with a wide range of paints and finishes, making it ideal for vehicle bumpers.
Plastic is the preferred material for modern car bumpers for several reasons. First and foremost, plastic is much lighter and more aerodynamic than metal, which improves the car's fuel efficiency. Plastic is also easier to shape, which is useful during both the manufacturing and bumper repair process.
Bumpers of most modern automobiles have been made of a combination of polycarbonate (PC) and acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) called PC/ABS.
OBJECTIVE
- To design Bumper as per automotive industry Standard.
- Create tooling axis for the given CLASS-A surface.
- Create B Class and C Class surfaces
- Create final surface model and convert it into solid body using close surface command in the part design workbench.
- Perform draft analysis for both Class-A surface and Final part body.
DESIGN METHODOLOGY
Skin data would be provided to us by the styling team to us.
Class-A surface means visible surface. It gives the aesthetic of the component which is created by the styling team and gives to the part design engineer to create the part with all engineering aspects.

The first step is to check the continuity of the class A surface. This is to ensure that there is no gap between surfaces. If we find any then we should fix that first.
Class-A continuity check
Analyse the class A surface through visual inspection.
To make sure that the given surface has no gap in between them. We can check it also with the help of Join or boundary commands.

Procedure for creating the tooling axis
Tooling axis represents the opening and closing of the mold core and cavity during the manufacturing of the components. A plastic product designer should consider the best tooling direction to cutdown the cost of the component very less.
Method opted for creating tooling axis for the bumper
- Check the best tooling direction for the given surface.
- We can find out the best tooling direction by cross checking all the three axes.



- Here we can find out that the best tooling direction for the pumper class-A surface is along x-axis direction
- The method I choose to create the tooling axis is first extracted a surface and create a midpoint on that surface. The introduced an axis system on that point.
- Then created a with the point and direction along x axis.
- Here both the outer flanges have 5.1-degree draft with respect to the axis created. Hence going with the axis created will not make any difficulties during the draft analysis.


- Another method is by creating intersection along y direction. And then create lines on the walls and then create a bisecting line with the lines on the wall and point created earlier. We will get an axis which will satisfy the draft analysis requirement.

Draft analysis for the given CLASS-A surface
The Draft Analysis is a command enables you to detect if the part you drafted will be easily removed. This type of analysis is performed based on colour ranges identifying zones on the analysed element where the deviation from the draft direction at any point, corresponds to specified values.
Draft analysis is done after determining the tooling axis, draft analysis is used to check whether the minimum draft (3 degrees) is maintained or not.
- Procedure for performing the draft analysis are as follows
- Change the view mode of the component to be in customized parameter mode and then select the shading mode as materials.

- Then open the featured draft analysis tool from the insert menu.

- Then click on use the compass to define the current drafting direction and then drag and align the compass on the Tooling axis.

- Then lock the draft direction and perform draft analysis by clicking on the component.

- The green colour shows the positive daft tooling direction and the given surface passes the draft analysis.
- Click on the analyses under the running point to check the draft analysis on the individual faces. It shows how much draft on specific points when we move the cursor point.

SURFACE-B CREATION
Class-B surface means thickness of a part it is not visible and is inside part. In other words, Class-B surface is a surface below a certain thickness from the class-A surface. This is the surface that contains engineering aspects of a model.
- Offset the class-A surface to 3mm inward direction.
- Rework on the patches and discontinuity of the offset surfaces using the features like extract, multi-extract, sweep, multi-section surfaces, extrapolate.
- To ensure the continuity of the Class-B surfaces check the boundary command to find out the boundary.
- Hence class-B surface creation is done.



SURFACE-C Creation
Surface that joins class-A and class-B surfaces is class-C surface. Class C is often specified for interior surfaces not readily visible, surfaces that will be covered by another part when assembled
Since it is a complex class-A surface, we cannot simply create the class-A boundary curve and sweep it at one shot. Hence, we need to create smaller curves using multi-extract command and then create sweep of 90 degree with reference to the surface option. sweeps at the midportion of the bumper should have a 93 degree vaue to pass the draft analysis.

- Extrapolate and trim off the sweep surface corners at the required edges.


- Join the sweeps using the join command and the class-c surface is created.

Creating the final surface of Bumper
- First step is to join the CLASS-A surface with CLASS-C surface.
- Then Trim the Joined surface with CLASS-B surface to achieve the final Bumper surface.

Go to the part design work bench and using the close surface command create the base bracket solid part body

3D Part model in various orientations (Isometric, Front, Side, and Top View)

The expanded Tree Structure for the geometrical set and the Part Body





Draft analysis of the Final part body
Same procedure for the draft analysis of CLASS-A surface is followed.
- Change the view mode to material shading
- Align the Compass with Tooling axis.
- Lock the draft direction and perform the Draft analysis.
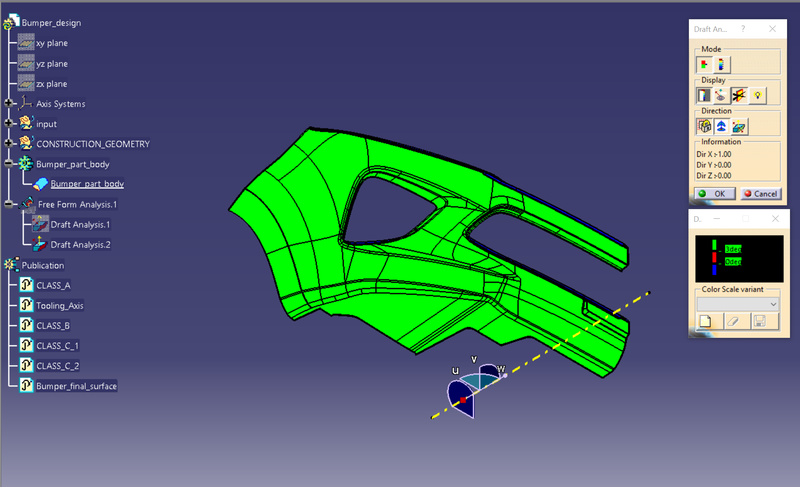



Conclusion
I have successfully created the class-B and Class-C surfaces of Bumper using the given Class-A surface along with the tooling axis in the CATIA surface workbench.
Leave a comment
Thanks for choosing to leave a comment. Please keep in mind that all the comments are moderated as per our comment policy, and your email will not be published for privacy reasons. Please leave a personal & meaningful conversation.
Other comments...
Be the first to add a comment
Read more Projects by Karthik S (27)
Project 2
AUTOMOTIVE WIRING HARNESS BACKDOOR Statement of assignment: Route the Wiring harness on Given car body and Prepare flatten view drawing in CATIA V5. Application of all Packaging rules, Industry best practices studied in this course shall be demonstrated in design. Apply Protection coverings as required. Available connector…
24 May 2023 03:20 PM IST
Project 1
AIM Route the Wiring harness on Given Engine and Prepare flatten view drawing in CATIA V5. Application of all Packaging rules, Industry best practices studied in this course shall be demonstrated in design. Apply Protection coverings as required. ENGINE WIRING HARNESS ROUTING …
23 May 2023 03:27 PM IST
Wiring harness design in CATIA V5 - 3D modeling Week 7 Challenge
AIM: TO FLATTEN THE WIRING HARNESS AND DRAFT THE WIRING HARNESS ASSEMBLY. GIVEN: HARNESS ASSEMBLY: HARNESS FLATTENING: WE GO TO THE HARNESS FLATTENING WORKBENCH AND DEFINE THE FLATTENING PARAMETERS. WE USE THE EXTRACT COMMAND TO BRING THE HARNESS ASSEMBLY TO THE FLATTENING WORKBENCH HERE. CHOOSING A SUITABLE PLANE WE FLATTEN…
13 May 2023 09:10 AM IST
Wiring harness design in CATIA V5 - 3D modeling Week 5 & 6 Challenge
modelling Week 5 & 6 Challenge Aim: Route two electrical harnesses per the given layout and interconnect them as a single harness assembly check for bundle continuity, and bundle warnings, and then provide annotations for the final harness assembly. Objective: The objective of this project is to first route the two Harness…
12 May 2023 08:28 AM IST
Related Courses



Skill-Lync offers industry relevant advanced engineering courses for engineering students by partnering with industry experts.
Our Company
4th Floor, BLOCK-B, Velachery - Tambaram Main Rd, Ram Nagar South, Madipakkam, Chennai, Tamil Nadu 600042.
Top Individual Courses
Top PG Programs
Skill-Lync Plus
Trending Blogs
© 2025 Skill-Lync Inc. All Rights Reserved.










